Welcome to the Amira-Avizo Software Use Case Gallery
Below you will find a collection of use cases of our 3D data visualization and analysis software. These use cases include scientific publications, articles, papers, posters, presentations or even videos that show how Amira-Avizo Software is used to address various scientific and industrial research topics.
Use the Domain selector to filter by main application area, and use the Search box to enter keywords related to specific topics you are interested in.
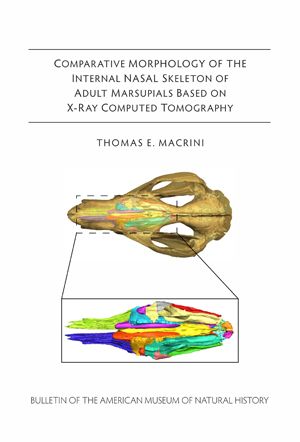
The internal skeleton of the nasal cavity is sporadically and often incompletely described for many marsupial species and mammals in general. Here, I provide an anatomical survey of the ethmoid in the skulls of adult marsupials based on examination of computed tomography (CT) imagery of 29 taxa representing all the major extant groups of marsupials. (…) I compared ecological data with the number of ecto- and endoturbinals as a preliminary test to determine whether some of the interspec... Read more
Thomas E. Macrini
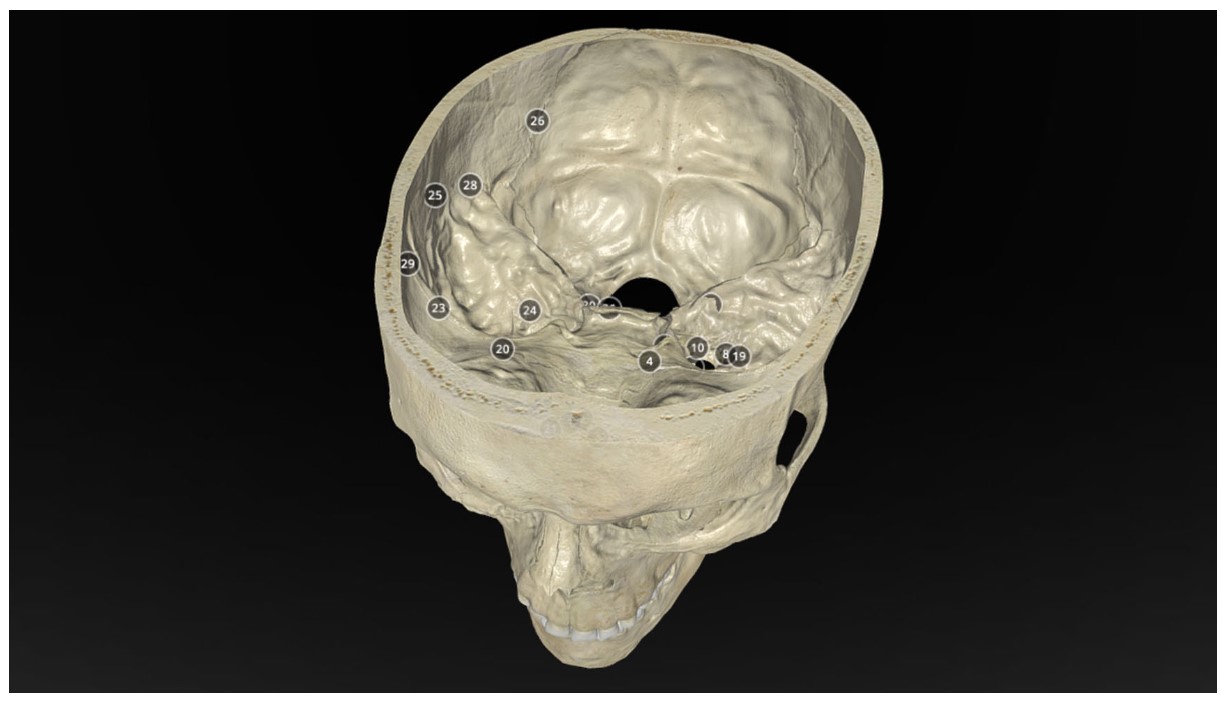
Operative Anatomy of the Human Skull: A Virtual Reality Expedition
Benjamin K Hendricks, MD Akash J Patel, MD Jerome Hartman Mark F Seifert, PhD Aaron Cohen-Gadol, MD, MSc, MBA
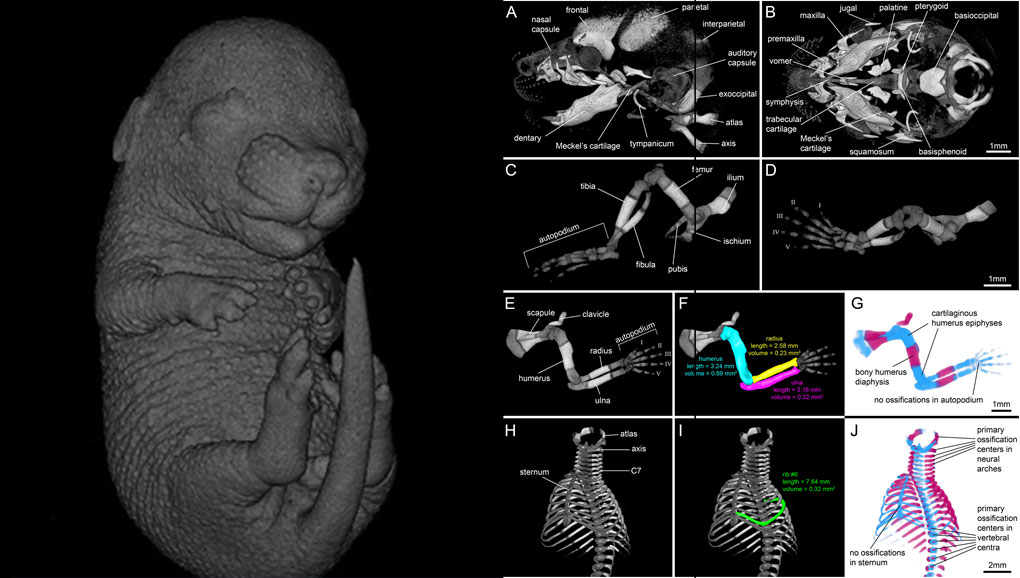
For decades, clearing and staining with Alcian Blue and Alizarin Red has been the gold standard to image vertebrate skeletal development. Here, we present an alternate approach to visualise bone and cartilage based on X-ray microCT imaging, which allows the collection of genuine 3D data of the entire developing skeleton at micron resolution.
Our novel protocol is based on ethanol fixation and staining with Ruthenium Red, and efficiently contrasts cartilage matrix, as demonstrated in wh... Read more
Simone Gabner, Peter Böck, Dieter Fink, Martin Glösmann, Stephan Handschuh
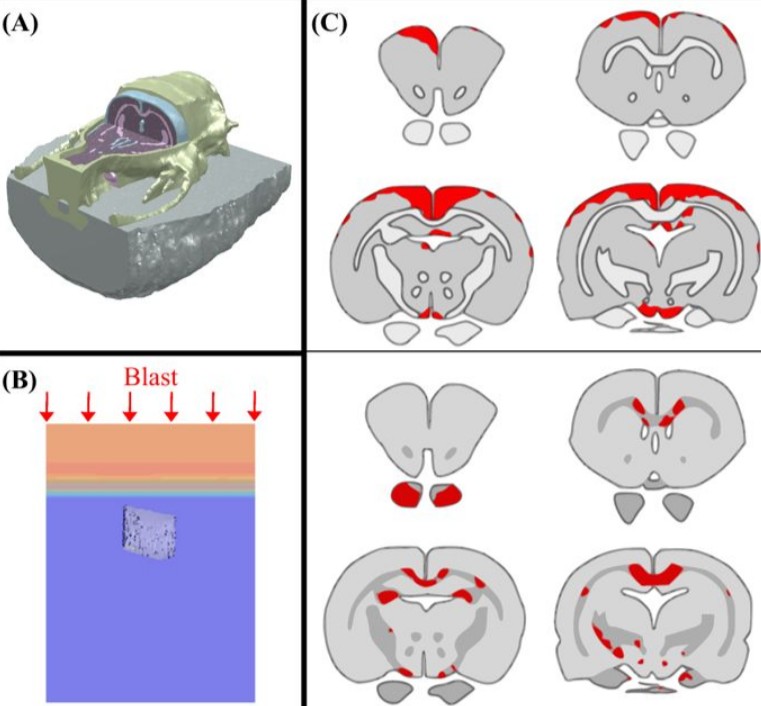
Cognition based bTBI mechanistic criteria; a tool for preventive and therapeutic innovations
Blast-induced traumatic brain injury has been associated with neurodegenerative and neuropsychiatric disorders. To date, although damage due to oxidative stress appears to be important, the specific mechanistic causes of such disorders remain elusive. Here, to determine the mechanical variables governing the tissue damage eventually cascading into cognitive deficits, we performed a study on the mechanics of rat brain under blast conditions. To this end, experiments were carried out to analyse... Read more
Daniel Garcia-Gonzalez, Nicholas S. Race, Natalie L. Voets, Damian R. Jenkins, Stamatios N. Sotiropoulos, Glen Acosta, Marcela Cruz-Haces, Jonathan Tang, Riyi Shi & Antoine Jérusalem
University of York student wins Anatomical Society Best Image Prize using Amira-Avizo Software
PhD student Jesse Hennekam wins for his reconstruction of the skull of a giant dormouse.
A York PhD student has won a prestigious award for his work reconstructing the skull of a giant rodent.
Jesse Hennekam, from the Centre for Anatomical and Human Sciences at the Hull York Medical School, created a digital reconstruction of the skull of a gigantic dormouse (Leithia melitensis), which roamed on the island of Sicily during the Pleistocene, roughly 2 million years ago... Read more
Jesse Hennekam
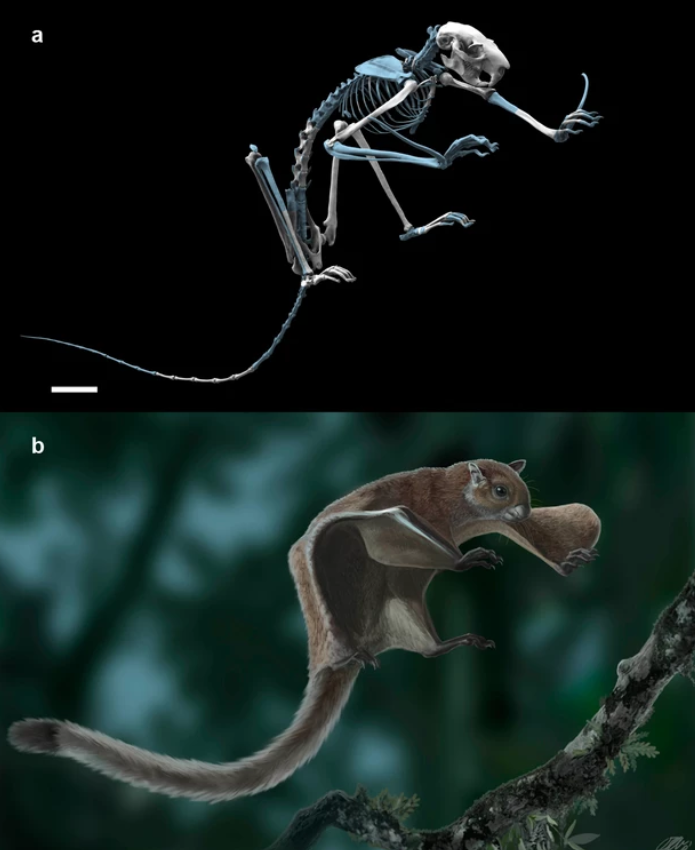

Oldest skeleton of a fossil flying squirrel casts new light on the phylogeny of the group
Here we report the oldest fossil skeleton of a flying squirrel (11.6 Ma) that displays the gliding-related diagnostic features shared by extant forms and allows for a recalibration of the divergence time between tree and flying squirrels. Our phylogenetic analyses combining morphological and molecular data generally support older dates than previous molecular estimates (~23 Ma), being congruent with the inclusion of some of the earliest fossils (~36 Ma) into this clade. They also show that fl... Read more
Isaac Casanovas-Vilar, Joan Garcia-Porta, Josep Fortuny, Oscar Sanisidro, Jerome Prieto, Marina Querejeta, Sergio Llacer, Josep M Robles, Federico Bernardini, David M Alba
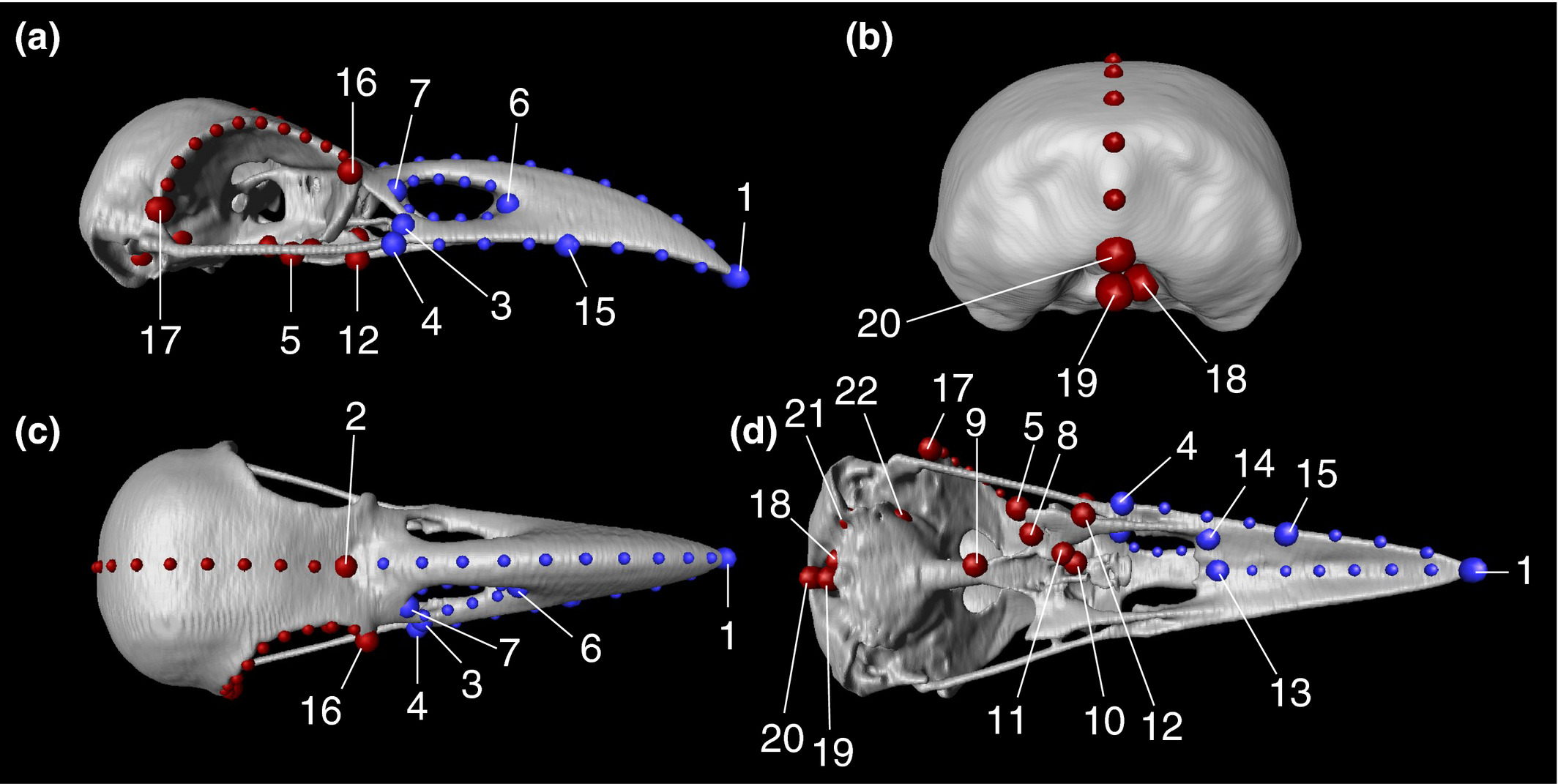
Here, to evaluate the intensity of evolutionary constraints on avian beak shape more appropriately, we selected large billed (Corvus macrorhynchos) and carrion crows (Corvus corone) as study objects. These landbird species seem to experience selection pressures favoring a departure from an allometric trajectory. A landmark based geometric morphometric approach using three dimensional reconstructions of CT scan images revealed that only 45.4% of the total shape variation was explained by allom... Read more
Takeshi Yamasaki, Sou Aoki, Masayoshi Tokita
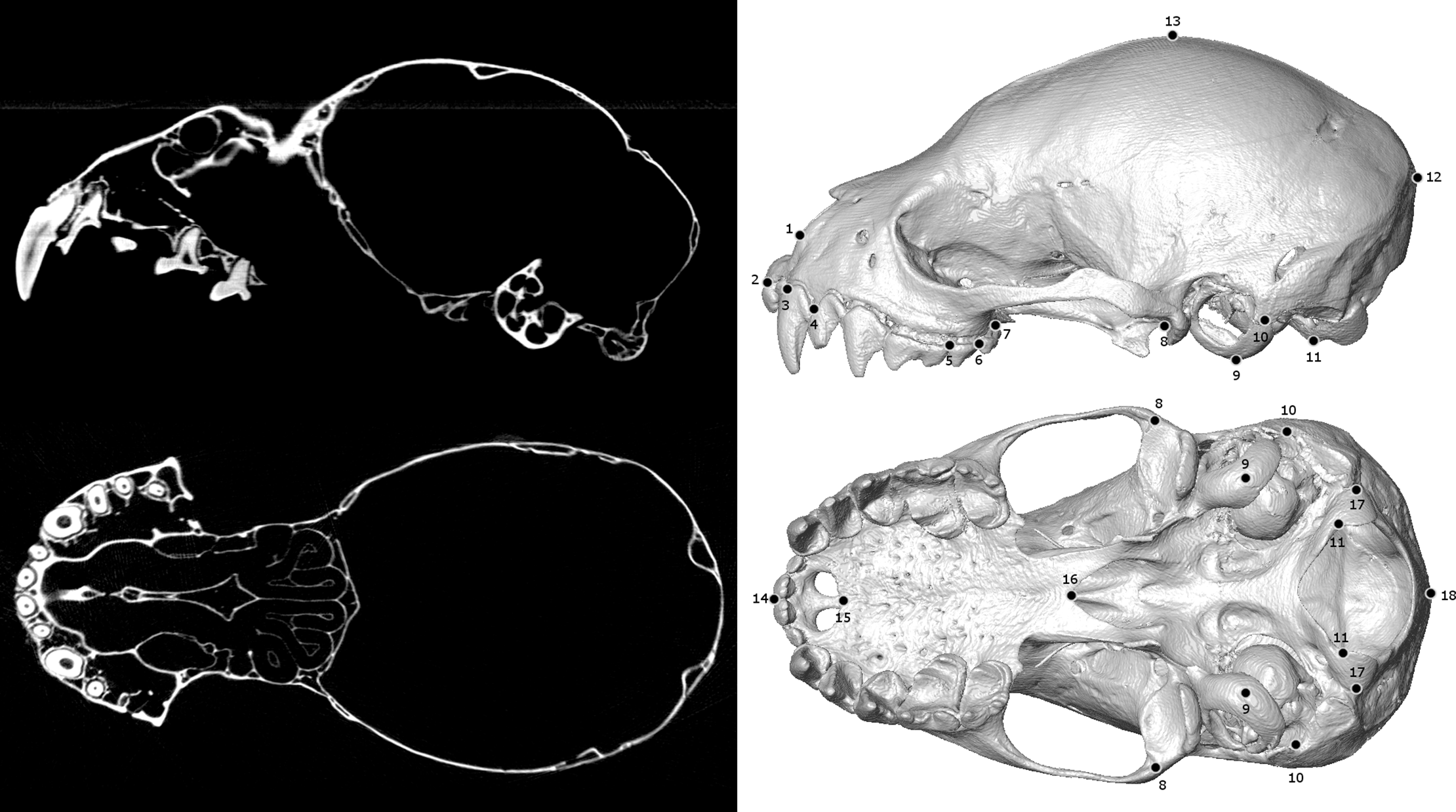
Biological specimens are primary records of organismal ecology and history. As such, museum collections are invaluable repositories for testing ecological and evolutionary hypotheses across the tree of life. Digitizing and broadly sharing the phenotypic data from these collections serves to expand the traditional reach of museums, enabling widespread data sharing, collaboration, and education at an unprecedented scale. In recent years, μCT-scanning has been adopted as one way for efficiently... Read more
Jeff J. Shi, Erin P. Westeen, Daniel L. Rabosky
The Faroe Islands are a group of islands in the North Atlantic that are known for its natural beauty, Viking culture and a special population of house mouse. The Faroese house mouse from the most remote island of the Faroese, Mykines (population: 10 people), looked so distinct when it was discovered that it was declared a subspecies, Mus musculus faeroenesis. These mice are large-bodied and showed an extreme form of left-right asymmetry in its skull. Our research group has... Read more
Yingguang Frank Chan, William H. Beluch, Rémi Blanc
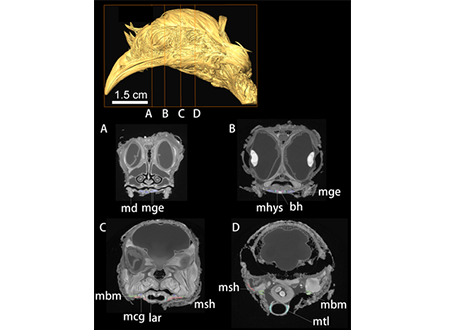
Convergent evolution of a mobile bony tongue in flighted dinosaurs and pterosaurs
The tongue, with fleshy, muscular, and bony components, is an innovation of the earliest land-dwelling vertebrates with key functions in both feeding and respiration. Here, we bring together evidence from preserved hyoid elements from dinosaurs and outgroup archosaurs, including pterosaurs, with enhanced contrast x-ray computed tomography data from extant taxa. Midline ossification is a key component of the origin of an avian hyoid. The elaboration of the avian tongue includes the evolution o... Read more
Zhiheng Li, Zhonghe Zhou, Julia A. Clarke
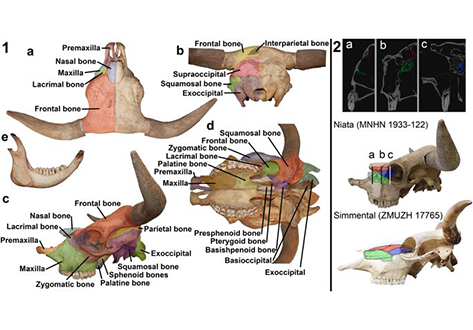
The Niata was a cattle variety from South America that figured prominently in writings on evolution by Charles Darwin. Its shortened head and other aspects of its unusual morphology have been subject of unsettled discussions since Darwin’s time. Here, we examine the anatomy, cranial shape, skull biomechanics, and population genetics of the Niata. Our results show that the Niata was a viable variety of cattle and exhibited anatomical differences to known chondrodysplastic forms. In cranial s... Read more
Kristof Veitschegger, Laura A. B. Wilson, Beatrice Nussberger, Glauco Camenisch, Lukas F. Keller, Stephen Wroe, Marcelo R. Sánchez-Villagra
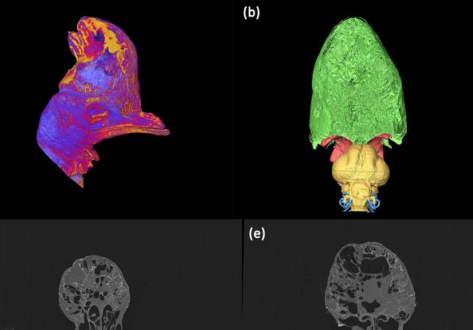
Cranial ornaments such as keratinous horns and bony casques are commonplace amongst birds and take a variety of diverse forms. Possible functions include display, thermoregulation, vocalisation and intraspecific combat, yet few hypotheses have been directly tested. Here we investigate the anatomy and mechanics of the casque of the Southern Cassowary (Casuarius casuarius), and test functional hypotheses using CT-based virtual dissection.
In particular, we determine the nature of pneumat... Read more
Charlotte A. Brassey , Thomas O’Mahoney
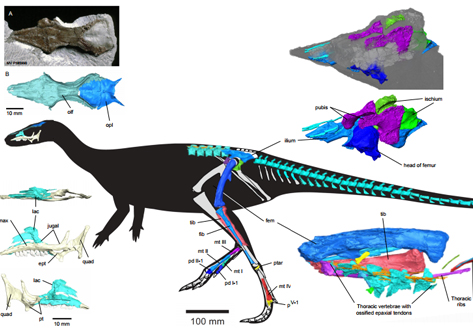
Revealing the skeleton of polar dinosaur using synchrotron computed tomography
Leaellynasaura amicagraphica was a small, bipedal, herbivorous dinosaur from the Early Cretaceous (~106 million years ago) of Australia within the Antarctic Circle of that time.
Synchrotron scans, and the resulting 3D reconstruction of the skull and post-cranial skeleton, provide a unique view of the morphology of Leaellynasaura, and allows this material to be 3D printed for display.
Read more
1University College London, UK; Monash University, Melbourne, Australia; Museum Victoria, Melbourne, Australia
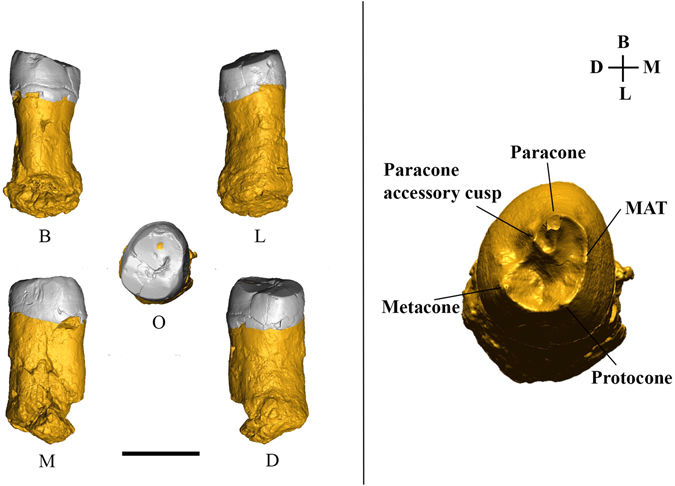
The first Neanderthal remains from an open-air Middle Palaeolithic site in the Levant
The late Middle Palaeolithic (MP) settlement patterns in the Levant included the repeated use of caves and open landscape sites. The fossil record shows that two types of hominins occupied the region during this period—Neandertals and Homo sapiens. Until recently, diagnostic fossil remains were found only at cave sites. Because the two populations in this region left similar material cultural remains, it was impossible to attribute any open-air site to either species. In this study... Read more
Ella Been, Erella Hovers, Ravid Ekshtain, Ariel Malinski-Buller, Nuha Agha, Alon Barash, Daniella E. Bar-Yosef Mayer, Stefano Benazzi, Jean-Jacques Hublin, Lihi Levin, Noam Greenbaum, Netta Mitki, Gregorio Oxilia, Naomi Porat, Joel Roskin, Michalle Soudack, Reuven Yeshurun, Ruth Shahack-Gross, Nadav Nir, Mareike C. Stahlschmidt, Yoel Rak & Omry Barzilai

The terrestrial Judith River Formation of northern Montana was deposited over an approximately 4 Myr interval during the Campanian (Late Cretaceous). Despite having been prospected and collected continuously by palaeontologists for over a century, few relatively complete dinosaur skeletons have been recovered from this unit to date. Here we describe a new genus and species of ankylosaurine dinosaur, Zuul crurivastator, from the Coal Ridge Member of the Judith River Formation, based ... Read more
Victoria M. Arbour, David C. Evans
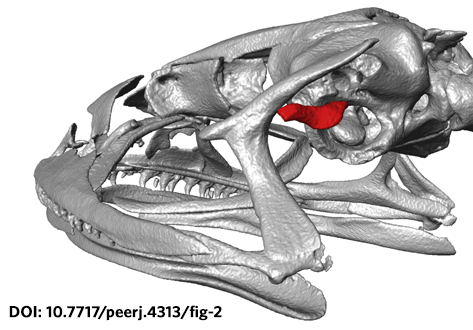
The loss of hearing structures and loss of advertisement calls in many terrestrial breeding frogs (Strabomantidae) living at high elevations in South America are common and intriguing phenomena. The Andean frog genus Phrynopus Peters, 1873 has undergone an evolutionary radiation in which most species lack the tympanic membrane and tympanic annulus, yet the phylogenetic relationships among species in this group remain largely unknown. Here, we present an expanded molecular phylogeny o... Read more
May R, Lehr E, Rabosky DL. PeerJ 6:e4313